This post could also have been titled confusion with foreach or For-EachObject
The scenario – Having created a blank database a number of users and permissions for an external consultant to create a test database for an application I got a phone call.
Please can you drop all the tables from the database as we need to re-run the installer with some different parameters
Sure, I thought. No problem. I will use PowerShell. A simple script is all I need
That ought to do it. Loop through the tables and drop each one. But when I ran it I got this error
What I did (which I should have done first up but time pressures hadn’t allowed) was drop the database and write a script to recreate it and all the users and permissions required using my Create Windows User Function and Add User to Database Role Function but it got me thinking.
So I went home and fired up my Azure VMs and had a play and found two ways of resolving it. But first lets understand what is happening here. I read this post which explains it quite well for his script.
We are going through a list collection and deleting any instance of our event receiver, in the “Foreach loop”. But once we delete an item we are modifying the current list collection. The “Foreach” loop looks to see what the current value is, before it moves on to the next item. But since we deleted the current item, we get the “Collection was modified; enumeration operation may not execute” error.
Now that understand what is going on, we can now look at a solution to correct the error.
The simplest way to avoid modifying the collection would be with a “For Loop”. With a “For Loop”, no modifications are made that will interrupt the looping process.
So when PowerShell has dropped the table it returns to the tables collection to find the current table before moving on to the next table but as we have deleted the table it falls over.
So lets fix it.
First lets create a test database with PowerShell. A piece of code that is useful to keep for scenarios like this. If you are creating a database for something other than a quick demo or a test then go and explore the other properties of the database object that you will surely want to configure. But for this demo the following is fine, it will use default options. The same applies for the tables script below.
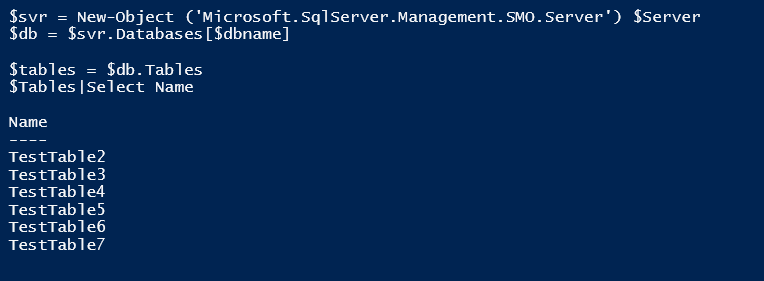
Now lets create some tables.
And check they have been created
Now following the advice from above we can do the following
First we count the number of tables and set it to a variable and then create a for loop. Note if you put $i –le $tables.Count then the script will only delete 4 tables! In the script block we are setting the $table variable to the first in the collection and then drops it. List the table names again to check or run $tables.Count and you will see that all the tables have been deleted.
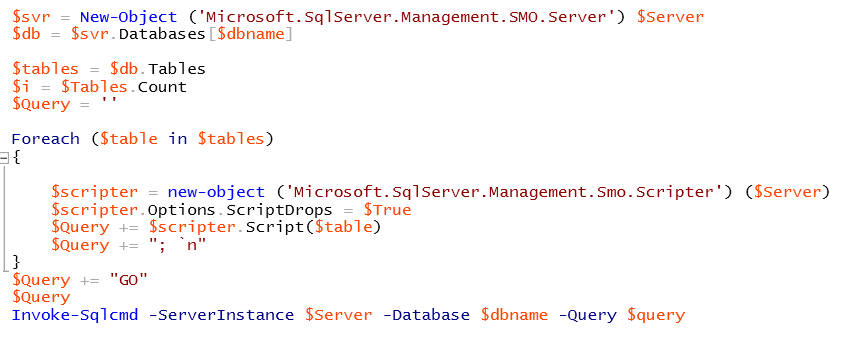
This was the other solution I found. It makes use of the scripter method to script the Drop commands for the tables add them to a Query string and pass that to Invoke-SQLCmd to run it.